Research Highlights
Latest Selected Publications & Visual Abstracts

Conditional Representation Learning for Customized Tasks
Spotlight, acc rate=3.2%
View Paper
Trustworthy Visual-Textual Retrieval
Trustworthy retrieval with uncertainty estimation.
View Paper
MaIR: A Locality- and Continuity-Preserving Mamba for Image Restoration
State-of-the-art image restoration using Mamba architecture.
View Paper
Trustworthy Visual-Textual Retrieval
Trustworthy retrieval with uncertainty estimation.
View Paper
MaIR: A Locality- and Continuity-Preserving Mamba for Image Restoration
State-of-the-art image restoration using Mamba architecture.
View Paper
Conditional Representation Learning for Customized Tasks
Spotlight, acc rate=3.2%
View PaperNoisy Correspondence
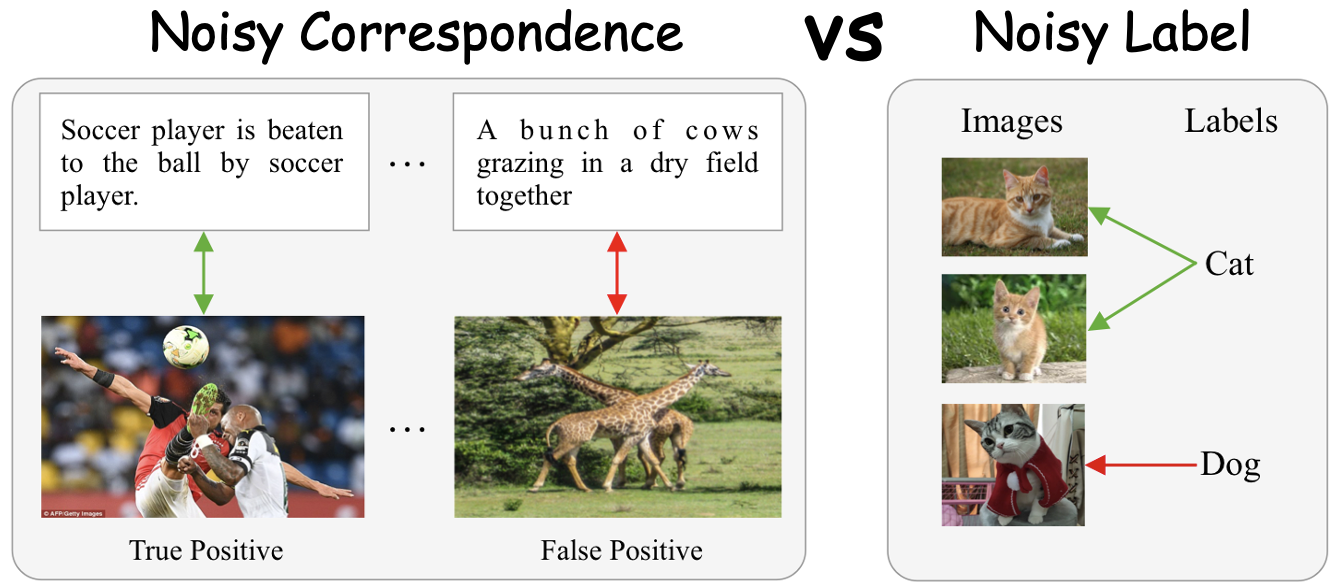
Noisy correspondence learning emerges as a new research DIRECTION of noisy label learning. Learning with Noisy Correspondence (NC) aims to address the mismatched pairs rather than typical annotation errors. Unlike traditional noisy label learning which primarily addresses incorrect annotations, NC shifts attention to incorrect correspondences between data samples, such as false positive and false negative correspondences.
The concept of NC was first formally introduced by XLearning group at NeurIPS 2021 (Oral presentation), which highlighted the negative impacts of mismatched pairs on learning foundation models CLIP. Since then, NC has been studied in numerous tasks, e.g., fundamental models, retrieval, Re-ID, QA, dialogue systems, graph matching, video reasoning (in CVPR'21, NeurIPS'21, CVPR'22, TPAMI'22, AAAI'23, CVPR'23, ICLR'24, NeurIPS'24 etc.).
Selected Publications
AI4LifeScience
XLearning Group is dedicated to addressing core interdisciplinary challenges and developing tailored solutions. Our current research efforts focus on AI4LifeScience (Nat. Comm.'23, Nat. Comm.'25) and the exploration of Virtual Cell models to advance the understanding of biological systems. We warmly welcome collaborations and discussions with teams across diverse disciplines.
Clustering
Clustering is a classic and fundamental problem in machine learning, focused on partitioning instances into distinct clusters based on their inherent semantics in an unsupervised manner, which is closely intertwined with unsupervised representation learning, as both seek to uncover latent structures in data. Clustering serves as a cornerstone for various real-world applications, including anomaly detection, community discovery, and bioinformatics, etc.
XLearning group proposed one of the first deep clustering methods (arxiv'15, IJCAI'16), which equips clustering algorithms with powerful discrimination ability to handle complex real-world data. In 2021, we proposed the contrastive clustering framework (AAAI'21, IJCV'22), which elegantly unifies representation learning and clustering by performing contrastive learning in the row and column spaces, respectively. Motivated by the classic k-means clustering algorithm, we designed the first interpretable unsupervised neural network, which is intrinsically explainable and transparent (JMLR'22). Recently, by looking back on the development of the clustering community, we wrote a survey that summarizes deep clustering methods from the prior perspective (Vicinagearth'24). Correspondingly, we propose a new externally guided clustering paradigm (ICML'24), seeking abundant yet regrettably overlooked external knowledge as priors to facilitate clustering.
Selected Publications